
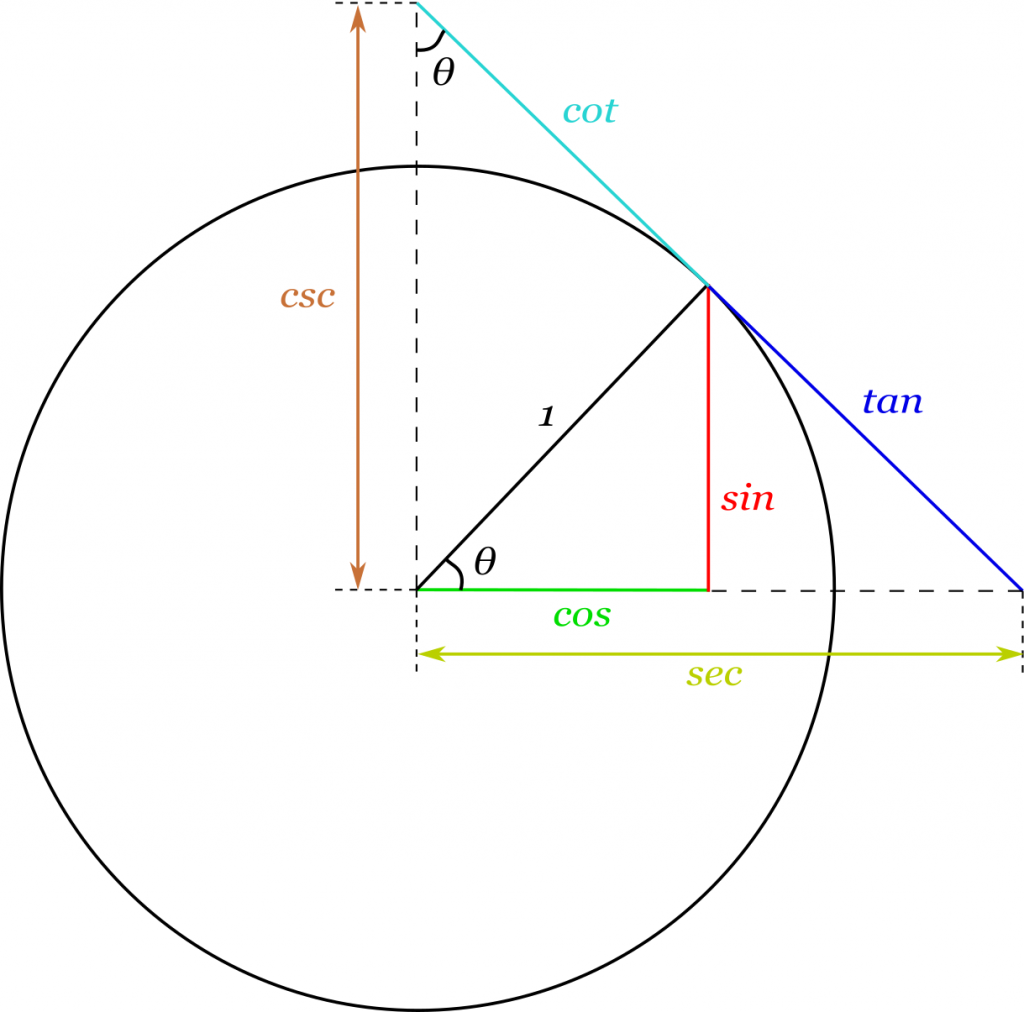
The obvious use of this surprising but true identity is to find the third side of a triangle given any two sides and the distance between them, or finding the angles given three sides.Defined by the equation x 2 + y 2 = 1 -axis. Sine, Cosine and Tangent (often shortened to sin, cos and tan) are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle: For a given angle each ratio stays the same. When solving right angled triangles with SOH CAH TOA, we considered values of sine, cosine and tangent. It was used by Ancient Greek mathematician and philosopher Pythagoras to prove his theory that a 2 + b 2 = c 2 Definition: The unit circle is a circle that is centered at the origin (0,0) & has a radius of one unit, and can be used to directly measure sine, cosine, &. Notes/Exercise: Grade 11 Trigonometry Unit circle. Also, since xcos and ysin, we get: (cos ())2 + (sin ())2 1. For example, finding out the new position of a sprite after it has moved some distance given its direction is impossible without trigonometry. Pythagoras' Theorem says that for a right angled triangle, the square of the long side equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides: x 2 + y 2 1 2.

The point of trigonometry is to be able to quickly relate angles to side lengths and vice-versa to do otherwise complex calculations. Trig (short for trigonometry) functions simply return the ratio of a certain two sides of a triangle, given one angle or the angle given a ratio of two sides. The longest side of a right triangle is also known as the 'hypotenuse.' The point where the hypotenuse touches the perimeter of the circle is at 3/2, 1/2. So, the longest side of this triangle will have a length of 1. This section introduces trigonometry in terms of what is called the wrapping function, which takes the real number line and wraps it around the unit circle. Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics which consists of the study of right-angled triangles - specifically, the ratios of sides of right-angled triangles. In a unit circle, any line that starts at the center of the circle and ends at its perimeter will have a length of 1. A sector of a circle is a pie shaped portion of the area of the circle. Below is unit circle with just the first quadrant filled in with the standard angles. Unfortunately, most people don’t learn it as well as they should in their trig class. For a straight line drawn from the circles centre point to a. The unit circle is one of the more useful tools to come out of a trig class. A unit circle is typically drawn around the origin (0,0) of a X,Y axes with a radius of 1.
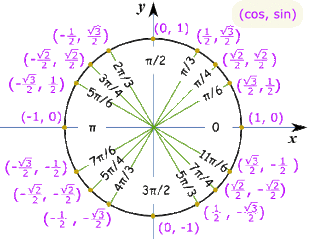

It can be used to evaluate trigonometric functions. The points on the graphs and the unit circle below were chosen so that there is a relationship between them. Let’s next take a look at one of the most overlooked ideas from a trig class. For more information, see Trigonometry on Wikipedia. The Trigonometry of Circles A sector of a circle: circle graphic. The Unit Circle is a circle centered at the origin with radius equal to 1. The unit circle concept takes any equivalence class of similar right triangles and represents the class using a single triangle with a hypotenuse of one.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
